Something I don’t quite get: it seems like this would grind the shit outta any surface it comes in contact with (or, be ground to shit if whatever’s on it is harder than the material of the cone thingies).
Does anyone have any idea how the constant abrasion is mitigated? Or is it somehow just not that big a deal, like it doesn’t actually chew chunks outta (for example) shoe soles?
Spent a lot of time with engineers, but am not one myself. Most grinding discs and things that wear stuff down have a surface made to rip in, and higher opposed friction. Think sandpaper, it digs into a surface with those hills from the grit, and uses the friction to then drag through cutting the surface and removing material.
With this floor, it looks like the wheels are smooth, so all though there’s some friction, it isn’t a cutting action. There’s also the fact that their friction is unopposed and can actually move the person, so the energy gets converted into movement, not the cutting force that would grind things down.
They really are just tiny treadmills, the only reason they’re discs is so they can be tilted to change the direction the “treadmill” is going to push you. If the disc is tilted to the right, the left most edge is going forward, if the disk is tilted to the left, that right edge is moving backwards. Otherwise exact same principle as a treadmill of creating friction to move the object on it.
Hope that helps some. Diagrams would probably help more.
If you ever run barefoot or in socks on a regular treadmill, you’ll feel that it’s a little bit rougher than just walking around normally. But it’s still not enough to really make noticeable wear on shoes (any more than normal running on pavement is).
Basically, shoe soles are specifically made to be pretty tough, so this type of treadmill shouldn’t be worse than normal.
It doesn’t grind anything basically the same way a treadmill doesn’t sand anything. You’re not forcing anything to stay put on the surface, you’re maneuvering on the surface while the surface is counter-moving you.
MKBHD’s video shows it moving him around on a chair, spinning the chair, etc etc. In the closeup shots, it looks like there’s debris on the surface of the cone thingies:
The debris isn’t uniform and is quite obviously not part of the roller material; I just kind of assumed that it was from stuff they’d been testing on it, though I suppose it could be generic workshop crud that fell on the rollers too 🤷
There’s probably very minimal sliding against that surface. From the point of view of each point of contact, it’s mostly static friction, with very little dynamic friction/slippage.
What… they aren’t spinning at high speeds and “grinding” the surface that’s on them. They only spin as quickly as they need to move the surface. Imagine a treadmill, it’s not going quicker than you are running on it, your shoes never slide on the surface, same here.
I really don’t understand how you have misunderstood this so badly.
If you watch MKBHD’s video, you see him spinning himself around on a chair. The chair legs are in constant contact with some part of the cone thingies while they’re rolling, which means friction, which means wear. I posted a screenshot from MKBHD’s video in another response that shows what looks like debris all over the surface of the cone rollers; the debris is not uniform and is quite clearly not part of the roller material (I put a screenshot in the reply to another comment, so I’ll just link it here), so I assumed that it was from testing the treadmill with various objects.
Yeah, there’s friction, just like there is friction from walking on marble steps, such as those in the Tower of Pisa. But since they are mostly moving with the object on top of them, wear is reduced. In the end, the little wheels will be working in concert to move whatever object is on them in a given direction, but they are round and so will have a bit of drift in short order, which is managed by putting the wheels at angles so only a portion of one side is touching the object. They are likely made of a moderate friction substance with high durability and are probably replaceable, just like the tires on your car.
Something I don’t quite get: it seems like this would grind the shit outta any surface it comes in contact with (or, be ground to shit if whatever’s on it is harder than the material of the cone thingies).
Does anyone have any idea how the constant abrasion is mitigated? Or is it somehow just not that big a deal, like it doesn’t actually chew chunks outta (for example) shoe soles?
Spent a lot of time with engineers, but am not one myself. Most grinding discs and things that wear stuff down have a surface made to rip in, and higher opposed friction. Think sandpaper, it digs into a surface with those hills from the grit, and uses the friction to then drag through cutting the surface and removing material.
With this floor, it looks like the wheels are smooth, so all though there’s some friction, it isn’t a cutting action. There’s also the fact that their friction is unopposed and can actually move the person, so the energy gets converted into movement, not the cutting force that would grind things down.
They really are just tiny treadmills, the only reason they’re discs is so they can be tilted to change the direction the “treadmill” is going to push you. If the disc is tilted to the right, the left most edge is going forward, if the disk is tilted to the left, that right edge is moving backwards. Otherwise exact same principle as a treadmill of creating friction to move the object on it.
Hope that helps some. Diagrams would probably help more.
If you ever run barefoot or in socks on a regular treadmill, you’ll feel that it’s a little bit rougher than just walking around normally. But it’s still not enough to really make noticeable wear on shoes (any more than normal running on pavement is).
Basically, shoe soles are specifically made to be pretty tough, so this type of treadmill shouldn’t be worse than normal.
It doesn’t grind anything basically the same way a treadmill doesn’t sand anything. You’re not forcing anything to stay put on the surface, you’re maneuvering on the surface while the surface is counter-moving you.
MKBHD’s video shows it moving him around on a chair, spinning the chair, etc etc. In the closeup shots, it looks like there’s debris on the surface of the cone thingies: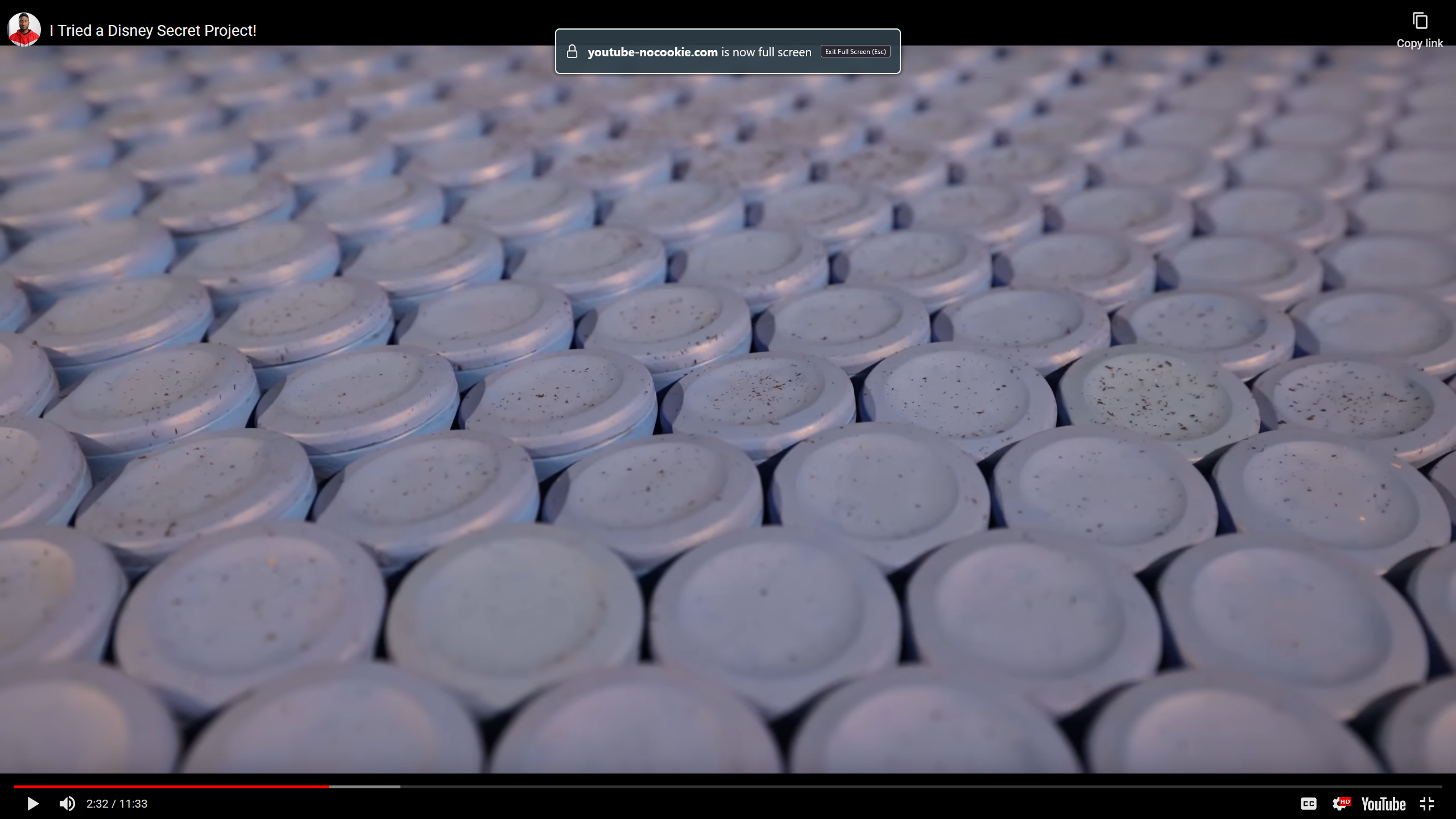
The debris isn’t uniform and is quite obviously not part of the roller material; I just kind of assumed that it was from stuff they’d been testing on it, though I suppose it could be generic workshop crud that fell on the rollers too 🤷
There’s probably very minimal sliding against that surface. From the point of view of each point of contact, it’s mostly static friction, with very little dynamic friction/slippage.
What… they aren’t spinning at high speeds and “grinding” the surface that’s on them. They only spin as quickly as they need to move the surface. Imagine a treadmill, it’s not going quicker than you are running on it, your shoes never slide on the surface, same here.
I really don’t understand how you have misunderstood this so badly.
If you watch MKBHD’s video, you see him spinning himself around on a chair. The chair legs are in constant contact with some part of the cone thingies while they’re rolling, which means friction, which means wear. I posted a screenshot from MKBHD’s video in another response that shows what looks like debris all over the surface of the cone rollers; the debris is not uniform and is quite clearly not part of the roller material (I put a screenshot in the reply to another comment, so I’ll just link it here), so I assumed that it was from testing the treadmill with various objects.
As well, there was no need to be a dick about it.
Yeah, there’s friction, just like there is friction from walking on marble steps, such as those in the Tower of Pisa. But since they are mostly moving with the object on top of them, wear is reduced. In the end, the little wheels will be working in concert to move whatever object is on them in a given direction, but they are round and so will have a bit of drift in short order, which is managed by putting the wheels at angles so only a portion of one side is touching the object. They are likely made of a moderate friction substance with high durability and are probably replaceable, just like the tires on your car.